Brainstem Electric Response with Audiometry
What is a BAER Test?
The brainstem auditory evoked response (BAER) test detects how the brain processes sounds that a person hears. The BAER test measures your brainwaves in reaction to clicks or other audio tones presented to you. A brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEP) or auditory brainstem response (ABR) test is another name for this examination.
A BAER test may help diagnose hearing loss and nervous system disorders, especially in infants, children, and individuals who are unable to take a conventional hearing test.
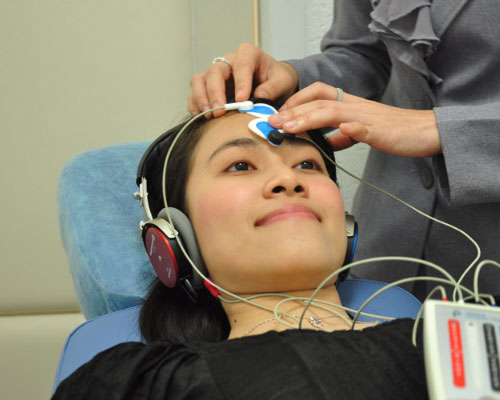
Brain Evoked Response Auditory (BERA) is a hearing test for children aged one to three years. Meanwhile, for children of a younger age, an OtoAcoustic Emission (OAE) test may be performed. If the BERA test results are in excellent condition, it is possible to infer that the child’s hearing function is within normal ranges and that no additional medical treatment is required. If the BERA test findings are found to be abnormal, the evaluation will proceed with the estimate or prediction of the hearing threshold, and hearing rehabilitation must begin as soon as feasible utilising hearing aids. The BERA exam will last about one hour.
Why should you take the BERA Test?
BAER is used to diagnose acoustic neuroma, instrinsic brainstem lesions (e.g., multiple sclerosis, infarction, gliomas), and hearing loss.Hearing loss in youngsters is difficult to detect at first. Speech, linguistic, cognitive, social, and emotional issues may all be exacerbated by hearing loss. As a result, it is preferable to conduct a hearing test on youngsters as soon as possible.
When the auditory nerve is able to transfer sound impulses from the ear to the brain at a particular pace, this is referred to as healthy hearing. The BERA test may determine if nerves transmit sound impulses to the brain and whether sound delivery speed is within normal limits. This hearing test may identify the kind of problem (conductive or sensorineural), severity (hearing threshold), and location of the child’s hearing loss (inner ear or other regions).
Procedure
BERA may be performed without requiring the patient to do anything. Patients simply need to lie down, ideally calmly or while asleep. This examination may be performed on children when they are awake, asleep, or under anaesthesia (although rarely). During the BERA test, electrodes will be put on the patient’s head and behind the ear. After the assessment, the patient will be exposed to clicking sounds through headphones. This test assesses variations in brain electrical activity (EEG) in response to auditory stimulation. Hearing loss is indicated by abnormalities in the transmission of signals when sound is heard.
Are there any side effects with the BERA test?
There are no risks associated with this exam, it is painless, and it does not require any special preparation for the BERA test.
Get a consultation on BERA Test with Dr. Poornima Shah – Neurophysiologist call now 9820238329 | 9321366625