What is Radiculopathy?
Radiculopathy is often caused by “wear and tear” changes in the spine that occur as people age. When it comes to trauma or injury, it is most typically caused by a rapid movement that results in a herniated disc, torn ligaments, or the formation of scar tissue that blocks a canal, nerve pathway, or exit zone.
In most situations, conservative treatment such as medication and physical therapy is effective in treating cervical radiculopathy.
Symptoms
The pain of cervical radiculopathy usually begins in the neck and proceeds down the arm to the region serviced by the injured nerve. This kind of pain is often characterised as burning or severe. Certain neck motions, such as stretching or straining the neck or moving the head, may aggravate the discomfort.
Other signs and symptoms include:
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensation in the fingers or hand
- Muscle weakness in the arm, shoulder, or hand
- Sensation loss
- Some patients say that placing their hands on top of their heads reduces their discomfort. This movement may ease pressure on the nerve root for a short time.
How Your Doctor Diagnoses Pinched Nerves?
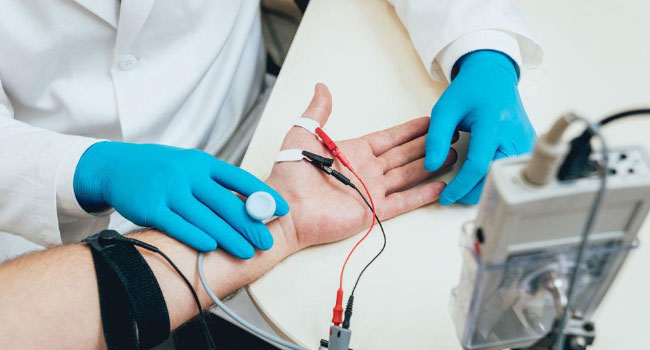
An EMG/NCV (Electromyography/Nerve Conduction Study) is the most reliable and exact test for diagnosing Pinched Nerves and developing a list of possible causes.
The EMG test assesses:
- nerves speed
- The amount of electricity that flows through the nerve.
- Nerve reaction time to stimulation
- overall pattern and function of the peripheral nervous system
Your doctor may recommend a 3T MRI to examine the anatomical structures and visually look for nerve flow obstructions, known as pinched nerves or impingement syndrome, in your neck, back, shoulder, leg, foot, or hand, which may be causing your symptoms of numbness, tingling, weakness, or cold or heat sensation.
Imaging studies do not replace the information obtained from an EMG test. Together, these numerous examinations and tests will provide your doctor with a more comprehensive picture of where your nerve is pinched and identify areas of malfunction, inflammation, and compression.
Electromyography
Electromyography is a technique that detects the electrical impulses of muscles both at rest and during contractions. A nerve conduction study is often performed in conjunction with EMG to establish whether a nerve is behaving properly. These are the most important diagnostic tests you can get to determine nerve malfunction or damage. They will assist your doctor in determining if your symptoms are the result of pressure on spinal nerve roots and nerve damage or another disorder that causes nerve damage, such as diabetes. These tests are recommended by physicians, orthopedic or spine surgeons to determine precisely where you have nerve compression, irritation, edoema, or decreased or non-conduction of the nerve. This information is essential because it helps them to choose the best therapy or procedure to restore your health and decrease your discomfort or pain.